Introduction
Injection molding is one of the most widely used manufacturing processes in the plastics industry. The selection of the right plastic is of crucial importance here, as it has a significant influence on the entire injection molding process, the quality of the manufactured parts and the cost-effectiveness of the project. In view of the large number of plastics available on the market, the question arises: Which plastic is best suited for injection molding? This article provides a comprehensive overview of the most common injection molding materials, their properties and applications, as well as current trends and innovations in the field of sustainable plastics processing.
Overview of plastic types in injection molding
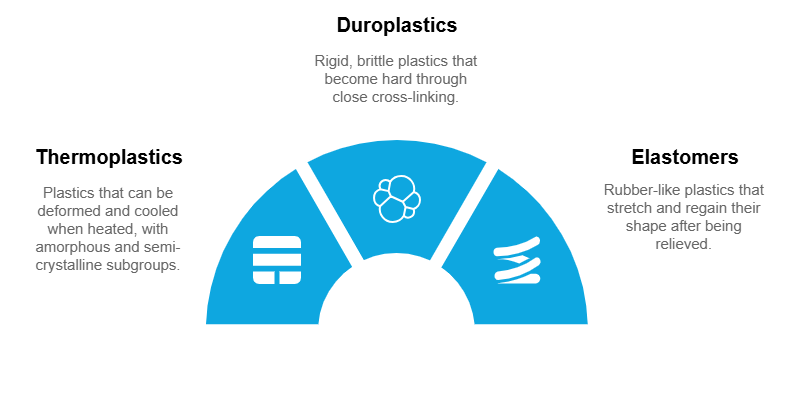
Thermoplastics
Thermoplastics are the most commonly used materials in the injection molding process. Their ability to melt when heated and solidify again when cooled enables repeated molding, which is particularly advantageous for mass production. Thermoplastics are one of the three main categories of plastics and can be divided into amorphous and semi-crystalline thermoplastics.
The special feature of amorphous thermoplastics is that they are crystal clear in their uncolored state. They are therefore particularly suitable for components that need to be transparent, e.g. transparent polycarbonate roofs for greenhouses or white or neutral polystyrene packaging for yoghurt pots. Semi-crystalline thermoplastics, on the other hand, have a color even in their uncolored state and form crystallites in their molecular structure. They usually have a white inherent color and can then be color-matched depending on their use. Examples of this are polyethylene (PE) or polypropylene (PP). These types of thermoplastics can then be used for colored toys, colored buttons on control elements or for packaging, for example.
Amorphe Thermoplastics
Polycarbonate offers excellent impact resistance and high dimensional stability. It is ideal for applications that require a robust and transparent material quality, such as hearing aid housings, spectacle lenses and bulletproof glass. Due to the bisphenol A it contains, PC is less suitable for food storage.
Polystyrene comes in two main varieties: high impact polystyrene (HIPS) and general purpose polystyrene (GPPS). GPPS is transparent and is often used for packaging and disposable items. HIPS is used in electronic housings and toolboxes. Even though they are often inexpensive, polystyrene rolls are not particularly environmentally friendly, as they are not biodegradable, for example.
Semi-crystalline thermoplastics
POM is an engineering thermoplastic known for its high rigidity, strength and low friction. It is often used in the manufacture of gears, fasteners and handle shapes. Despite its excellent mechanical properties, POM is not resistant to certain acids.
Acrylic glass impresses with its outstanding transparency and high tear resistance. It is a popular alternative to glass and is often used for windows, transparent housings and lighting elements. Acrylic is odorless and tasteless, which also makes it suitable for food packaging.
Nylon is characterized by high strength, toughness and excellent wear resistance. It is often used for automotive parts such as gears, bushings and bearing balls. Thanks to its high melting temperature and chemical resistance, nylon is particularly suitable for mechanically stressed applications.
ABS is a versatile plastic that is tough, dimensionally stable and impact-resistant. Due to its good bondability and mechanical properties, it is often used for electronic housings, automotive parts and toys. However, ABS can be prone to weld lines and sink marks, which can be reduced by blending with polycarbonate.
Polypropylene impresses with its high resistance to chemicals and moisture. It is flexible, wear-resistant and offers high impact strength, which makes it ideal for packaging, automotive parts and medical applications. However, PP can become brittle at low temperatures.
Polyethylene is light, tough and offers excellent electrical insulating properties. It is often used for household items, packaging and children's toys. Despite its lower strength, PE is a popular injection molding plastic due to its versatility and resistance to many chemicals.

(Thermoplastic) elastomers
TPU combines elastomeric properties with high tensile and tear strength. It is used for rubber-like parts, cable insulation and sporting goods. TPU is easy to process and can be molded at high temperatures.
TPE combines properties of rubber and thermoplastics, which makes them flexible and impact-resistant. They are often used for seals, flexible connections and soft handles. TPEs are recyclable and offer good resistance to chemicals and weathering.
Duroplastics
Thermosetting plastics, also known as thermosets, differ fundamentally from thermoplastics. They undergo irreversible hardening and can no longer be melted or reshaped after hardening. Thermosets offer high heat and chemical resistance, but are brittle and difficult to recycle. They are used in areas that require high temperature and chemical resistance, such as electronic housings, automotive parts and aircraft components.
Important criteria when selecting the plastic
The plastic must be able to withstand the mechanical and chemical requirements of the application. Parts that are exposed to high loads require more robust materials such as polycarbonate or nylon. In addition, care must be taken to ensure that the plastic in question can fulfill the shape of the injection-moulded part. Clean edges and precisely fitting radii are particularly important here. Depending on the density and flexibility of the plastic, however, the various design parameters are fulfilled with varying degrees of accuracy.
Find out more about the respective design parameters in our blog post on injection molding tips. We will also be happy to advise you on the best plastics for your project, taking your design requirements into account.
Properties such as strength, flexibility, impact strength and heat resistance are crucial. For example, thermoplastic elastomers offer high flexibility, while thermosets have excellent heat resistance.
Transparent plastics such as acrylic and polycarbonate are ideal for applications that require a clear appearance. Colored or opaque material can be achieved by choosing appropriate plastics and additives.
The material costs vary greatly between the different plastics. Polyethylene and polypropylene are often cheaper than polycarbonate or ABS, but offer different mechanical properties.
Sustainability in injection molding
With growing environmental awareness, sustainability is becoming increasingly important in plastics processing. This is reflected in the increased use of recycled plastics and bio-based materials.
Recycling injection molding enables the reuse of plastic waste. Material and cost savings can be realized through the use of regranulates. However, there are challenges in quality control and the consistency of the recycled materials.
Bioplastics, made from renewable raw materials such as corn starch, offer a more environmentally friendly alternative to conventional plastics. These materials are biodegradable and reduce the carbon footprint of production. However, their mechanical properties and processing techniques are still the subject of intensive research.
Companies are developing innovative processes for integrating recycled and bio-based materials into the injection molding process. These technologies improve process stability and material properties, making sustainable production both economical and qualitatively appealing.
Innovations and trends in injection molding
Despite its many years of use, injection molding technology remains dynamic and innovation-driven:
The integration of digital technologies enables more precise process monitoring and control. Intelligent tool sensors and automated systems improve the efficiency and quality of production.
Modern injection molding systems have advanced sensors and software solutions that provide real-time data and enable immediate adjustment of process parameters. This reduces reject rates and improves the consistency of the manufactured parts.
The expansion of the material portfolio to include new thermoplastics and thermosets as well as the development of hybrid materials enables the production of parts with specific requirements. This offers new opportunities in areas such as medical technology, the automotive industry and electronics.
Conclusion and future outlook
Choosing the right plastic is crucial for successful injection molding. Thermoplastics offer the largest market share due to their processing flexibility and repeatable molding, while thermosets are becoming increasingly important for special applications with high requirements. Ongoing digitalization and material innovation will continue to drive injection moulding technology forward, resulting in high-quality, sustainable and cost-effective solutions.
At assemblean, we make sure that we always keep an eye on future developments. In doing so, we not only pay attention to improved recycling processes, but also constantly expand our range of materials in order to meet your requirements in terms of sustainability and innovation. Find out more about our complete range on our injection molding page. We look forward to hearing from you!