1. Introduction to the injection molding process
Injection molding is a primary molding process in which thermoplastic or thermoset polymers are injected into a shaping cavity and removed as a finished part after cooling. This process enables the precise and repeatable production of plastic parts in large quantities. By controlling temperature, pressure and injection speed, high dimensional accuracy and surface quality can be achieved.The injection molding process
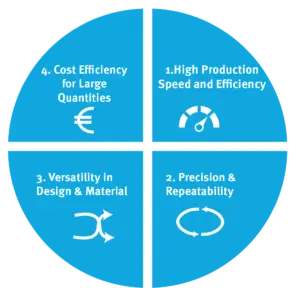
The process can be divided into the following steps:4 Advantages of Injection Molding
4 Cost Factors in the Injection Molding Process
1. Tooling CostsThe production of the injection mold is one of the biggest cost factors. These costs vary significantly depending on the complexity and size of the mold, ranging from a few thousand to several hundred thousand euros. Highly complex molds with multiple cavities and fine details require precise CNC machining or EDM techniques, increasing tooling costs. 2. Material Costs
The choice of plastic significantly affects costs. Standard materials such as polypropylene (PP) or polyethylene (PE) are more affordable, whereas engineering plastics like ABS or polycarbonate are more expensive. High-performance plastics that offer special properties such as high temperature resistance or increased strength also increase material costs. Our Material Overview can help you with your selection. 3. Production Volume
The higher the production volume, the lower the cost per part, as fixed costs are spread over more units. For very high quantities, injection molding is particularly cost-efficient, whereas in smaller series, the cost per unit is significantly higher. 4. Machine Technology
The type of injection molding machine (hydraulic, electric, or hybrid) also influences costs. Electric machines are more precise and energy-efficient but more expensive to purchase, whereas hydraulic machines are more robust but less precise and more energy-intensive. Hybrid machines combine both technologies, offering a balance between precision and robustness, albeit at higher initial costs.

2. Injection Molding vs. 3D Printing: A Comparison
Costs and Production VolumeInjection molding is more cost-efficient than 3D printing for high quantities (from 300-500 pieces). While injection molding is economical for large series, 3D printing offers advantages for small series and prototypes, as it does not require expensive tooling. The cost per unit is significantly lower with 3D printing at low volumes, whereas it decreases substantially in injection molding for high quantities. Design Complexity
3D printing allows for the production of complex and customized designs without the need for special tooling. This is particularly beneficial for one-off or custom parts. Injection molding, on the other hand, often requires extensive mold-making processes for complex geometries, increasing costs. For highly complex parts, 3D printing is the more flexible and cost-effective solution. Material Variety and Surface Quality
Injection molding offers a wider range of materials and higher surface quality, making it ideal for functional and aesthetic requirements. 3D printing still lags behind in this regard, though it continues to advance in material diversity and surface finish. Engineering plastics used in injection molding exhibit superior mechanical properties and more consistent surfaces. Production Speed
Injection molding has shorter cycle times compared to 3D printing in high-volume production, leading to faster large-scale manufacturing. In contrast, 3D printing excels in quick start-up times and flexibility for small series. For the production of large numbers of identical parts, injection molding is significantly faster.
3. When is Injection Molding Worth It?
High Quantities and Standardized PartsInjection molding is particularly beneficial for producing large quantities of identical parts, such as in the automotive, electronics, or consumer goods industries. The high efficiency and low unit costs at full production capacity are key advantages. Standardized parts benefit from the repeatability and precision of the process. High Precision and Quality Requirements
For parts that require high precision and consistent quality, injection molding is indispensable. Applications in medical technology or aerospace benefit from precise dimensional accuracy and surface quality. Technical requirements demand finely tuned process parameters and high-quality materials, which are best implemented through injection molding. Complex or Function-Integrated Parts
Injection molding enables the integration of multiple functions into a single part, such as insert elements or multi-component parts. This reduces assembly effort and increases the functionality of the final products. Complex geometries and multifunctional designs can be cost-efficiently realized through targeted mold design. Sustainability and Material Efficiency
Due to minimal material waste and the possibility of reusing excess material, the process contributes to sustainability. Regrinded material can be reused in specific percentages, reducing material costs and waste. Optimized process control and recycling further enhance ecological sustainability.
4. The Future of Injection Molding
Integration of Digital TechnologiesThe integration of digital technologies and automation will continue to optimize the molding process. Digital molds and intelligent production systems can improve efficiency and increase flexibility. The use of IoT and machine learning allows for process monitoring and optimization, leading to higher production quality and reduced downtime. Development of New Materials
The development of new, environmentally friendly, and high-performance plastics is expanding the application possibilities. Bioplastics and sustainable materials are gaining importance and offering new opportunities for the plastics industry. These materials allow for reducing the environmental footprint of production without compromising functional requirements. Collaboration with Additive Manufacturing
Injection molding and 3D printing are increasingly complementing each other rather than competing. 3D printing can be used for prototyping and small series, while injection molding is responsible for mass production. This synergy enables a flexible and cost-efficient production approach where both processes maximize their strengths.
Conclusion
The injection molding process offers numerous advantages for mass production of plastic parts, especially for high volumes, complex designs, and strict quality requirements. Despite high initial investments, it is cost-efficient and flexible in the long run. Combined with modern technologies and sustainable materials, it remains a key manufacturing method that we also utilize in our services.Do you have more questions or an idea for production? Then feel free to send us a request!