In modern manufacturing, plastics play an essential role, as they are indispensable components in nearly all areas of life and industries. Two of the most commonly used processes for producing plastic parts are injection molding and extrusion. Although both methods are used for plastic processing, they differ significantly in their processes, applications, and economic aspects. This article highlights the key differences between injection molding and extrusion to determine the best method for specific production requirements.
Fundamentals of Injection Molding and Extrusion
Injection Molding
Injection molding is a primary shaping process in which molten plastic is injected under high pressure into a mold cavity. This mold, consisting of two or more parts, defines the final shape of the plastic component. After injection, the plastic cools, solidifies, and is ejected from the mold, resulting in precise and complex three-dimensional parts.
Extrusion
Extrusion is a continuous forming process in which liquid plastic is pressed through a shaping die to create elongated, uniform profiles such as pipes, tubes, or films. Unlike injection molding, this is a continuous process that consistently processes material, which is then cut to the desired length.
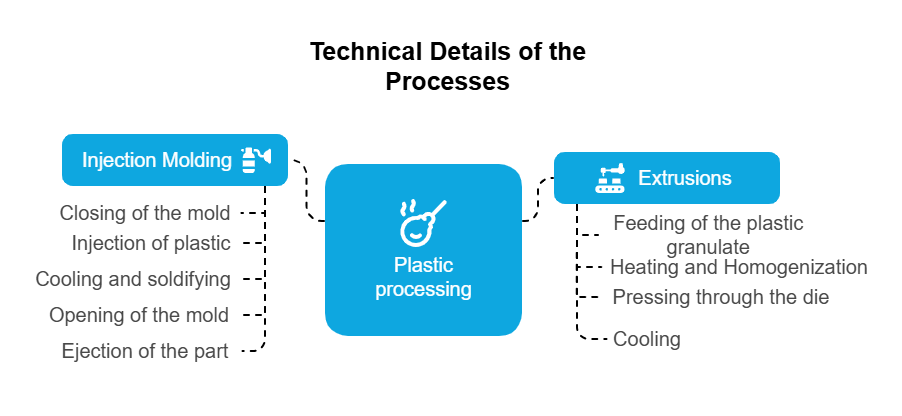
Technical Details of the Processes
Injection Molding Process
The injection molding process begins with closing the mold, into which plastic granules are fed through a hopper into a heated screw barrel. The screw melts, mixes, and injects the plastic into the mold under high pressure. After cooling, the plastic solidifies, the mold opens, and the finished part is ejected. Depending on the complexity of the part, this cycle can take only a few seconds, allowing for high production speeds.
Extrusion Process
In the extrusion process, plastic granules are continuously fed into a heated extruder. A screw mechanism melts and homogenizes the material, which is then pressed through a die that defines the desired shape. After exiting the die, the plastic cools and solidifies into a continuous profile. This process is particularly efficient for producing large quantities of uniform products with a consistent cross-section.
Material Requirements
Injection Molding
The injection molding process is highly versatile and can be used with various types of plastics, including thermoplastics, thermosets, and elastomers. Thermoplastics such as polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP) are particularly popular due to their ability to be melted and reshaped multiple times. Thermosets, on the other hand, undergo an irreversible curing process during injection molding and cannot be reshaped once hardened. Elastomers offer flexibility and are used for parts requiring some degree of stretchability. Further information for the material choice you can find here.
Extrusion
Extrusion is primarily suitable for thermoplastics such as polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polyethylene (PE), and polypropylene (PP). These plastics can be repeatedly melted and reshaped, making extrusion an ideal process for continuous production. The range of materials is less diverse than in injection molding but still sufficient for most extrusion applications.
Applications
Injection Molding
Injection molded parts are widely used in industries requiring precise and complex shapes. Typical applications include housings, automotive parts, medical devices, and electronic components. The high precision and repeatability of the injection molding process make it particularly suitable for mass production of identical parts with tight tolerances.
Extrusion
Extrusion is mainly used for manufacturing elongated profiles such as pipes, tubing, cable coatings, and films. In the construction industry, extruded profiles are commonly used for window frames and seals. Extruded films are also widely used in the packaging industry. Therefore, extrusion is ideal for the continuous production of large quantities of uniform products.
Pros and Cons of Injection Molding and Extrusion
Injection Molding
- High precision: Enables the production of complex and detailed shapes with tight tolerances.
- Versatile material use: Allows the use of thermoplastics, thermosets, and elastomers.
- High repeatability: Ensures consistent quality and uniformity of produced parts.
- High tooling costs: Mold production is expensive and time-consuming.
- Cost-effectiveness only at high volumes: Injection molding becomes economical only with sufficiently large production quantities.
Extrusion
- Cost-efficient for uniform products: Lower tooling costs and faster production processes.
- Continuous process: Ideal for the uninterrupted production of long profiles.
- Lower operating costs: Simpler workflows and less complex tooling.
- Limited shape capabilities: Mainly suited for uniform, two-dimensional shapes.
- Less precise: Lower dimensional accuracy compared to injection molding.

Costs
Injection molding requires a significant initial investment for mold production, which is made from hardened steel. Therefore, these costs are only amortized with high production volumes, making injection molding an economical choice for mass production. The more complex the shape, the higher the manufacturing costs and the time required for mold completion.
Extrusion, on the other hand, is more cost-effective to set up, as extrusion tools are simpler and quicker to manufacture. This makes extrusion particularly attractive for continuous production processes with constant cross-sections, where unit costs are reduced through high production volumes.
Future and Trends
The plastics industry is constantly evolving, with increasing emphasis on sustainability, recycling, and automation. In the field of injection molding, new materials are being explored to be more environmentally friendly and reusable. Additionally, advancements in digitalization and automation are further improving efficiency and precision.
In extrusion, the focus is on optimizing energy efficiency and reducing material waste. Innovative extruder designs and sustainable material flows contribute to improving process costs and environmental compatibility.
Conclusion
Injection molding and extrusion are fundamental processes in plastic manufacturing, each with its specific strengths and application areas. While injection molding is ideal for complex, three-dimensional parts and mass production due to its high precision and versatility, extrusion offers a cost-effective solution for the continuous production of uniform, elongated profiles.
The choice of the right process largely depends on the specific requirements of the project, the desired materials, the required precision, and the planned production volume. You can also read more about the injection molding process here.
You have more questions regarding injection molding or have a idea to produce? Then feel free to send us a request!